
NASA has confirmed the existence of a planet-wide ambipolar electric field, a phenomenon first hypothesized over 60 years ago, that plays a crucial role in Earth’s atmospheric dynamics. This discovery marks a significant advancement in our understanding of the forces that maintain Earth’s habitability, alongside gravity and the magnetic field.
60-Year-Old Hypothesis Confirmed

The ambipolar electric field, essential for preventing the drift of negatively charged electrons and positively charged ions, was first theorized in the late 1960s. Spacecraft flying over Earth’s poles detected a mysterious outflow of atmospheric particles into space. While some particle escape was expected due to solar radiation, scientists were puzzled by the discovery of a cold, supersonic polar wind that hadn’t been heated by the Sun. This anomaly led to the hypothesis that an unknown force was driving these particles into space, particularly above the North and South Poles.
Key Findings and Measurement Methodology
NASA’s 2022 Endurance mission finally provided concrete evidence of the ambipolar field. The mission involved launching a suborbital rocket from Svalbard, Norway, on May 11, 2022. The rocket, named Svalbard, reached an altitude of approximately 477 miles (768 kilometers) and recorded a 0.55-volt change in electric potential—equivalent to the strength of a watch battery. This minute measurement was enough to confirm the presence of the ambipolar electric field, proving its influence on Earth’s atmosphere.
The field plays a critical role in maintaining the balance between negatively charged electrons and positively charged ions in the atmosphere. This balance prevents these particles from drifting apart due to gravity, ensuring that the atmosphere remains stable.
The ambipolar field exerts a force on hydrogen ions that is 10.6 times stronger than gravity, enabling them to escape into space at supersonic speeds. For heavier particles like oxygen ions, the field reduces their weight, allowing them to reach altitudes previously considered impossible.
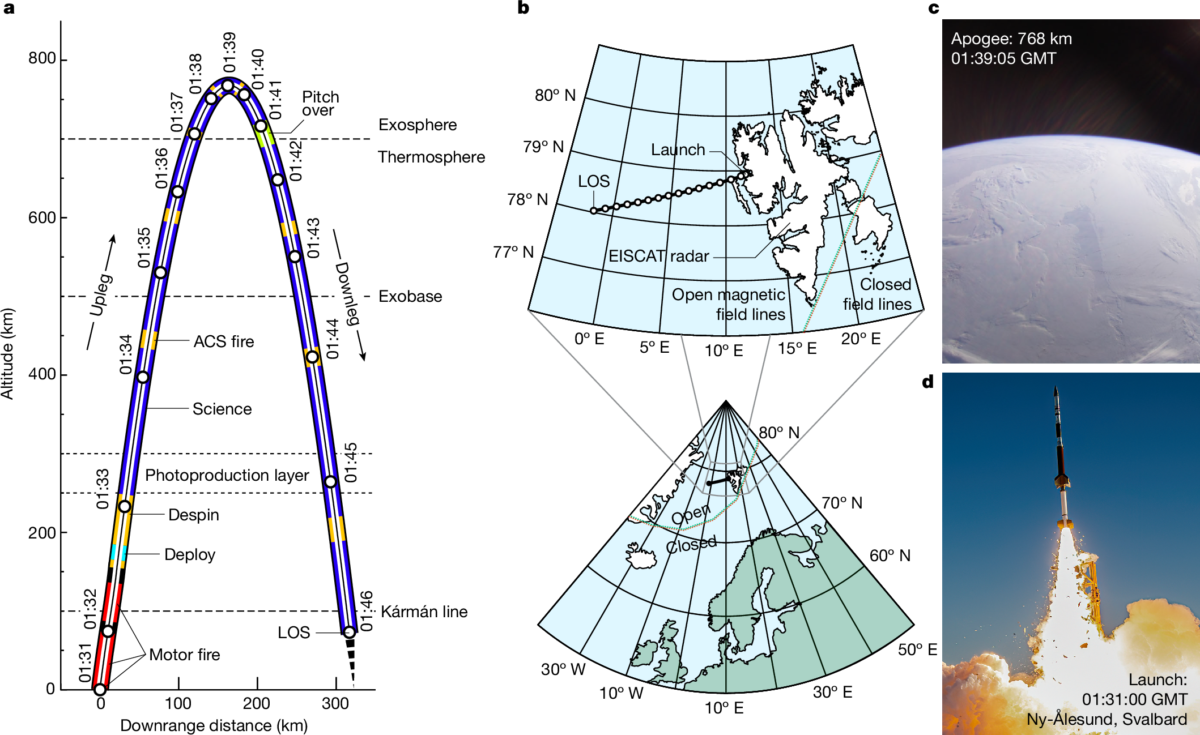
Key Findings from the Endurance Mission
- Ambipolar Electric Field: This weak, planet-wide electric field is as fundamental to Earth as gravity and magnetic fields. It was first hypothesized over 60 years ago and plays a crucial role in driving the “polar wind,” a continuous outflow of charged particles from Earth’s poles into space.
- Launch Details: The Endurance rocket launched on May 11, 2022, from Svalbard, Norway, reaching an altitude of 477.23 miles (768.03 kilometers) before splashing down in the Greenland Sea 19 minutes later.
- Measurements: The mission recorded a change in electric potential of just 0.55 volts, which, while seemingly small, is sufficient to explain the dynamics of the polar wind. The force exerted by the electric field on hydrogen ions is 10.6 times stronger than gravity, allowing them to escape into space at supersonic speeds.
- Impact on Atmospheric Science: The ambipolar electric field increases the scale height of the ionosphere by 271%, indicating that it can hold a denser atmosphere at greater altitudes. This discovery opens new avenues for exploring how electric fields shape planetary atmospheres, potentially existing on other planets like Venus and Mars.
- Technological Innovations: The mission utilized advanced instruments, including a photoelectron spectrometer, to measure the electric field with high precision, marking a significant advancement in atmospheric research technology.
Implications for Atmospheric Dynamics
The ambipolar electric field’s influence on atmospheric particles has profound implications for our understanding of Earth’s atmospheric dynamics.
Glyn Collinson, the principal investigator for NASA’s Endurance mission, described the field as a “conveyor belt” that lifts atmospheric particles into space. This discovery provides new insights into how Earth’s atmosphere has evolved over time and suggests that similar fields may exist on other planets with atmospheres, such as Venus and Mars.
Understanding Earth’s ambipolar electric field not only sheds light on the planet’s atmospheric evolution but also opens up new avenues for research into planetary habitability across the solar system.
The presence of similar electric fields on Venus and Mars could influence their atmospheric dynamics in ways that are not yet fully understood, potentially offering clues about the conditions necessary for life on other planets.
The detection of the ambipolar electric field marks a pivotal advancement in atmospheric science, providing critical insights into Earth’s history and the potential for life elsewhere in the solar system.
The findings from NASA’s Endurance mission, published in the August 2024 edition of Nature, offer a new understanding of how electric fields shape planetary atmospheres over time. As scientists continue to explore this phenomenon, the discovery promises to deepen our knowledge of both Earth and the broader cosmos.
References:
Earth’s ambipolar electrostatic field and its role in ion escape to space, Nature, 28 August 2024
NASA Discovers a Long-Sought Global Electric Field on Earth, Aug 28, 2024
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE: SHOCKING: UN Report Discusses Plans to Block Out the Sun







